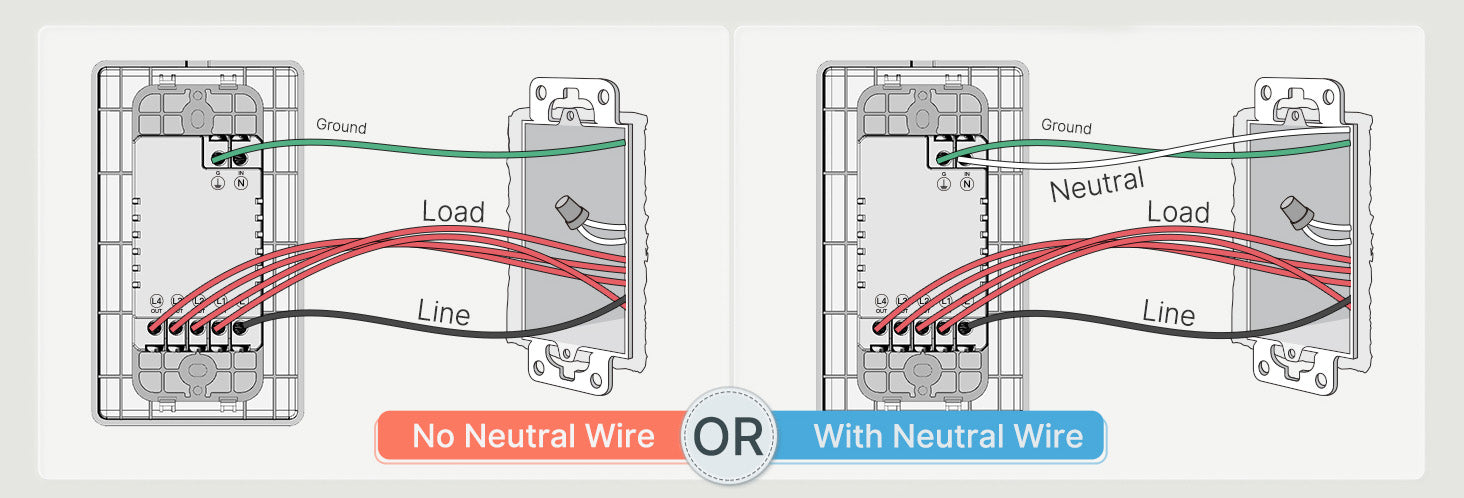
The wires in a switch box typically serve the purpose of controlling electrical currents to operate lights, fans, or other electrical devices. Here is a brief overview of common wire types found in MOES smart switch installations
Hot Wire (Line Wire)
- Made of a conductive material, typically copper or aluminum, to efficiently carry electrical current from the power source to the switch.
- Carries voltage from the power source
- Protected by circuit breakers or fuses to prevent excessive current flow that could lead to overheating and electrical fires.
- While black or red are the most common colors for hot wires, local electrical codes may allow other colors for specific applications.
- Identified by their connection to the brass-colored terminal screws on switches and receptacles. It's essential to connect hot wires to the appropriate terminals to ensure proper electrical function.
- Live when the circuit is energized, meaning they have the potential to deliver an electrical shock if touched or mishandled.
- Supplies electrical power to the switch, allowing it to control the flow of electricity to the connected load, such as a light fixture, appliance, or electrical outlet.

Neutral Wire
- Serves as a crucial component in electrical circuits by providing a return path for the electrical current to flow back to the power source.
- Typically carries voltage close to zero volts, as its primary function is to complete the circuit rather than supply power to the load.
- In most electrical installations, the neutral wire is identified by its white insulation.
- By providing a path for the current to return to the power source, the neutral wire helps prevent electrical shocks and ensures proper functioning of appliances and equipment.

- In multi-phase electrical systems, such as those found in residential and commercial buildings, the neutral wire helps balance the electrical load across phases.
- In some switch boxes, especially those controlling a single light fixture or outlet, the neutral wire may not be present.
- Some smart switches, dimmers, and other advanced devices may require a neutral wire for proper operation.
Ground Wire (Earth)
- Serves as a critical safety feature in electrical systems, ensuring the protection of individuals and property against electric shock and fire hazards.
- During a fault condition, such as a short circuit or equipment malfunction, the ground wire provides a low-resistance path for excess electrical current to safely dissipate into the earth.
- Typically constructed of bare copper or insulated with green insulation, ground wires are easily identifiable within electrical systems.
- Securely connected to the metal enclosure of switch boxes, electrical panels, outlets, and other metal components within the electrical system.
- Adherence to electrical codes and regulations mandates the inclusion of ground wires in electrical installations.
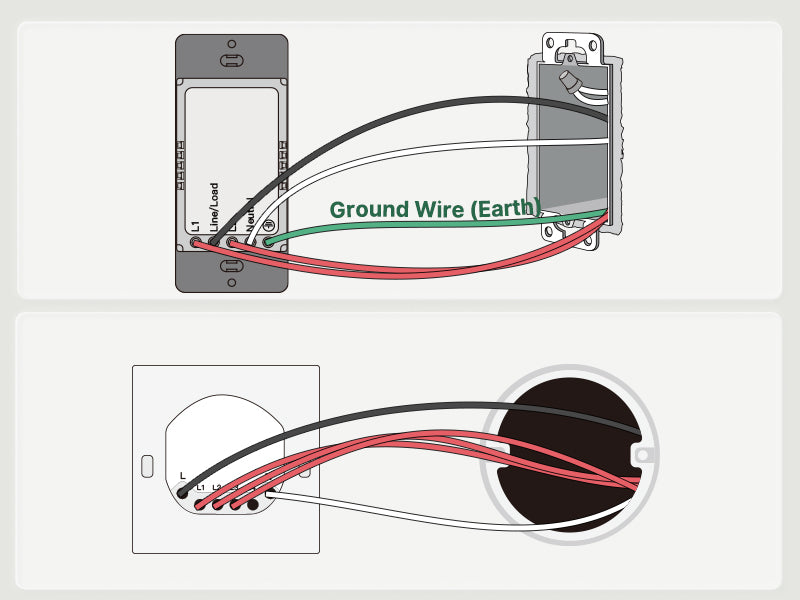
Traveler Wires
- Indispensable components in multi-switch setups, allowing for the control of a single electrical load from multiple switch locations.
- Red or black in color. When one switch changes the state (on/off) of the electrical load, the traveler wires convey this signal to the other switches, ensuring synchronized control.
- By enabling control from various entry points or strategic locations within a building, traveler wires enhance convenience and accessibility for occupants.
- In three-way switch systems, two traveler wires connect the switches, allowing control from two locations. Four-way switch systems utilize additional traveler wires to extend control to three or more locations, offering greater flexibility in lighting control.
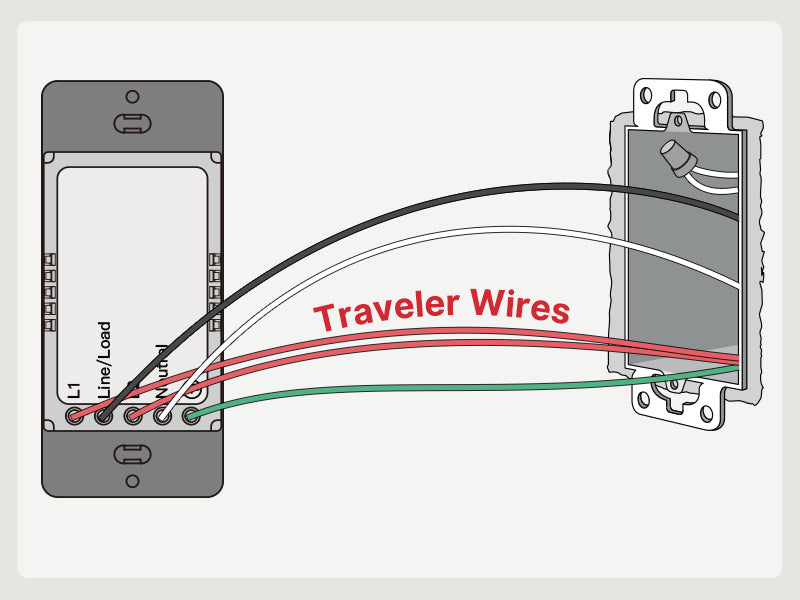
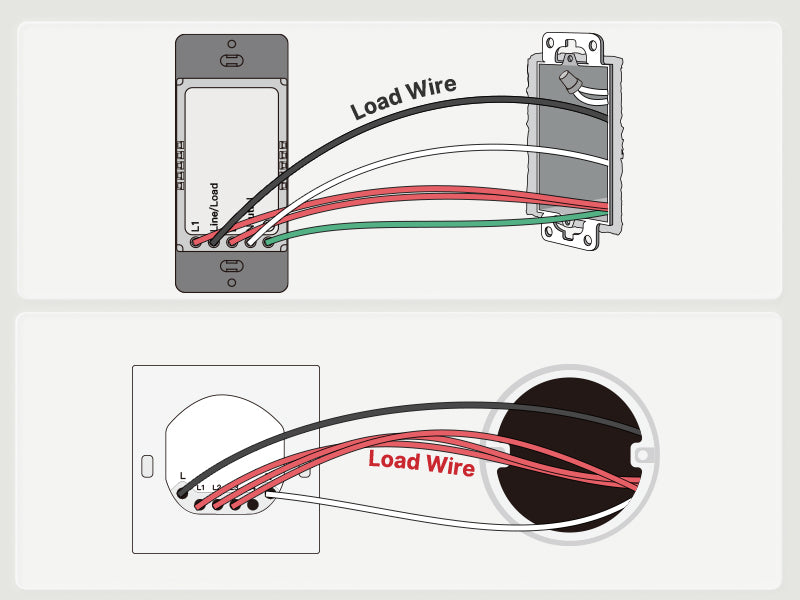
Load Wire
- Serves as the conduit for electrical power from the switch to the connected device, such as a light fixture, ceiling fan, or receptacle outlet.
- Often distinguished by its black color, the load wire is identifiable within the switch box and aids electricians in proper wiring connections.
- Upon activation of the switch, electrical current flows through the load wire to power the connected device, illuminating lights, activating fans, or energizing appliances.
- The load wire is securely attached, completing the circuit and enabling control of the electrical load. Proper termination ensures reliable operation and safety compliance.
Caution
If you lack experience with installing light switches or feel uneasy about working with line-voltage wiring, it's highly advisable to enlist the services of a qualified electrician. Ensuring the safe and proper installation of switches is paramount for your well-being and the integrity of your electrical system.
Prior to commencing any work, always use the circuit breaker to deactivate the power supply to the switch box. Refer to the appropriate breaker switch in your electrical panel to ensure complete isolation of the circuit. Here's a helpful guide on how to do this.
Please Note
The color of wires may not necessarily correspond to their intended function in your household wiring. Relying solely on wire color can lead to errors during installation.
Explore Our Smart Solutions Today!
A more reliable method for identifying wires is to reference the terminals on your old switch. By noting how wires were connected to specific terminals, you can better understand their intended roles in the circuit. This approach reduces the risk of miswiring and ensures a smoother installation process.
MOES offers a diverse range of smart switches, smart plugs, and smart curtain models to elevate your home automation experience. Whether you're looking to enhance convenience, energy efficiency, or security, our products are designed to meet your needs.
With easy installation, intuitive controls, and compatibility with popular smart home platforms, integrating MOES devices into your home is a seamless process.
From controlling lights and appliances remotely to automating your curtains for added comfort, MOES empowers you to create a smarter and more connected living space. Explore our selection today and discover the possibilities of a truly intelligent home.